Compound exercises are multi-joint movements that work different muscles groups at once. They are one of the most effective ways to build strength, increase muscle mass, and improve overall fitness. Incorporating compound exercises into your workout routine can help you achieve your fitness goals faster and more efficiently. In this article, I will discuss the best 5 compound exercises and how to perform them.
Compound exercises are movements that involve more than one joint and work multiple muscle groups at the same time. Unlike isolation exercises that target only one muscle group, compound exercises are more efficient and effective at building overall strength and muscle mass. Some of the benefits of compound exercises include improved athletic performance, increased metabolism, and reduced risk of injury.

The top 5 compound exercises are squat, deadlift, bench press, pull-up, and overhead press. These exercises work multiple muscle groups and are essential for building overall strength and muscle mass. In the following sections, I will discuss how to perform each exercise correctly and safely.
Key Takeaways
- Compound exercises are multi-joint movements that work different muscles groups at once.
- The top 5 compound exercises are squat, deadlift, bench press, pull-up, and overhead press.
- Incorporating compound exercises into your workout routine can help you achieve your fitness goals faster and more efficiently.
Understanding Compound Exercises
As someone who has been strength training for years, I have come to appreciate the power of compound exercises. Compound exercises are movements that work multiple muscle groups at the same time, making them incredibly efficient for building strength and muscle.
Unlike isolation exercises, which only work one muscle group at a time, compound exercises involve multiple joints and muscle groups. This means that you can lift heavier weights and work more muscles in less time.
Some of the benefits of compound exercises include:
- Increased strength and muscle mass
- Improved coordination and balance
- Reduced risk of injury
- Greater calorie burn during and after exercise
Some examples of compound exercises include squats, deadlifts, bench press, pull-ups, and lunges. These movements work a variety of muscle groups, including the legs, back, chest, shoulders, and arms.
It’s important to note that while compound exercises are incredibly effective, they can also be more challenging to perform than isolation exercises. Proper form is essential to prevent injury and maximize results.
In the next section, I will outline the top 5 compound exercises and provide step-by-step instructions on how to perform them correctly.
Best 5 Compound Exercises
As a fitness enthusiast, I have found that compound exercises are the most effective way to build muscle and strength. Compound exercises work multiple muscle groups at the same time, making them highly efficient and effective. Here are my top 5 compound exercises that I recommend for anyone looking to build muscle and strength.
1. Squat
The squat is widely considered the king of all exercises, and for good reason. It works the entire lower body, including the quads, hamstrings, and glutes, as well as the core and lower back. To perform a squat, stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, and lower your body by bending your knees and hips until your thighs are parallel to the ground. Then, push through your heels to return to the starting position.
2. Deadlift
The deadlift is another essential compound exercise that targets the entire posterior chain, including the hamstrings, glutes, and lower back. To perform a deadlift, stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, and place your hands on the barbell with an overhand grip. Lift the barbell off the ground by extending your hips and knees, keeping your back straight and your chest up. Lower the barbell back down to the ground by bending your hips and knees.
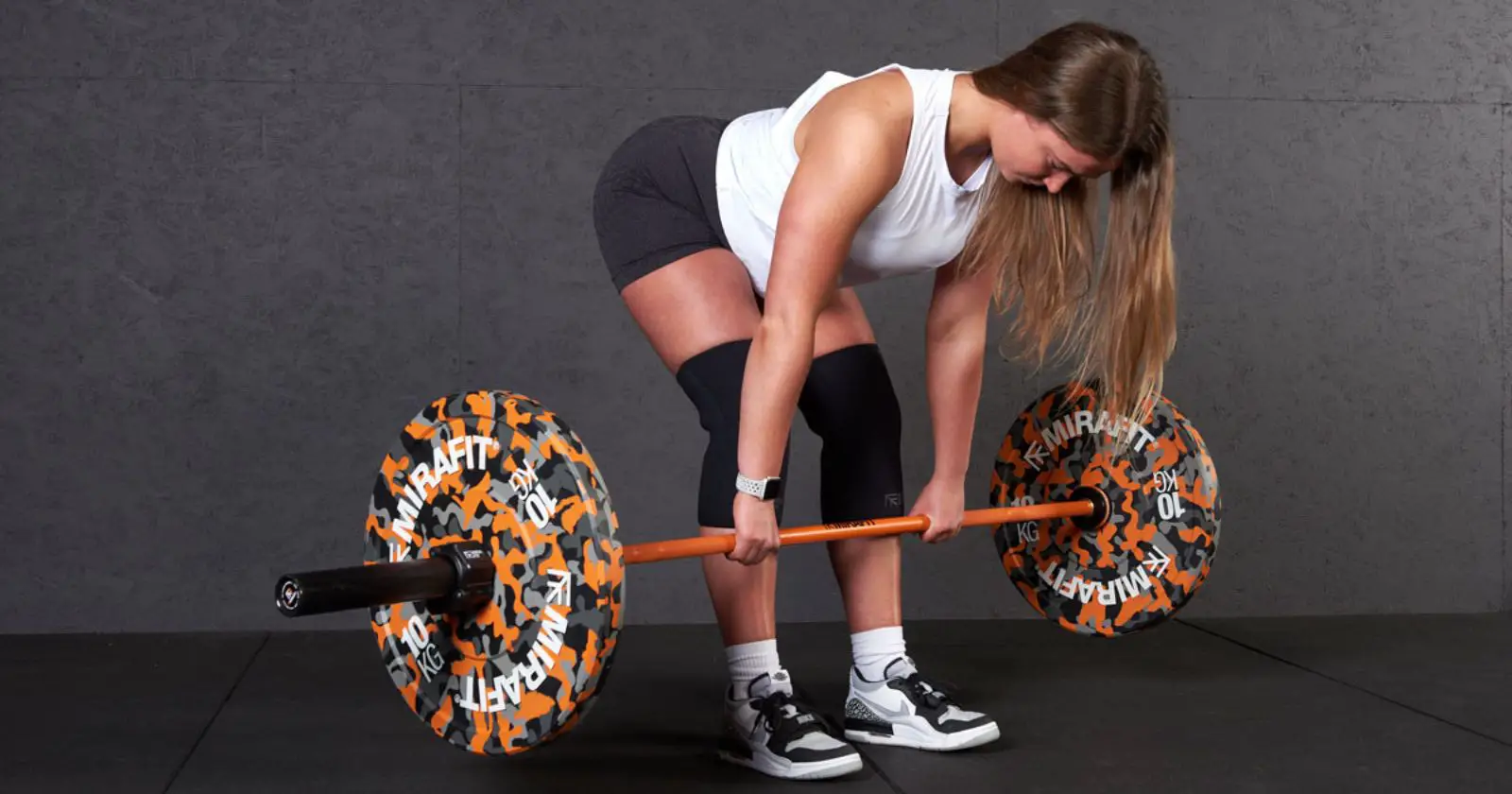

3. Bench Press
The bench press is a classic compound exercise that targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps. To perform a bench press, lie on a bench with your feet flat on the ground and your hands on the barbell with a shoulder-width grip. Lower the barbell to your chest, keeping your elbows tucked in, and then push the barbell back up to the starting position.

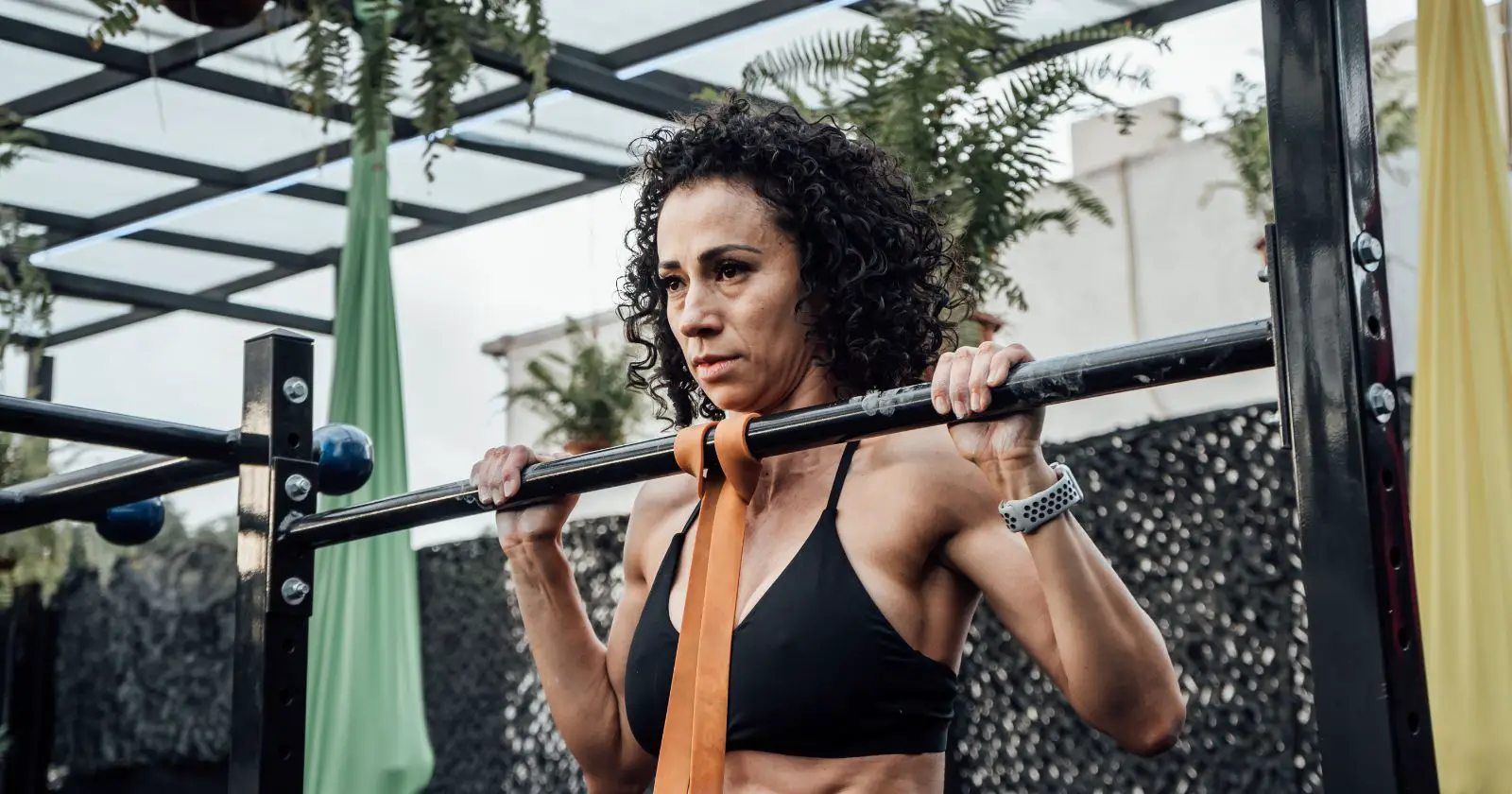
4. Pull-up
The pull-up is a challenging compound exercise that targets the back, shoulders, and biceps. To perform a pull-up, grip a pull-up bar with your palms facing away from you, and hang with your arms fully extended. Pull your body up until your chin is above the bar, and then lower yourself back down to the starting position.

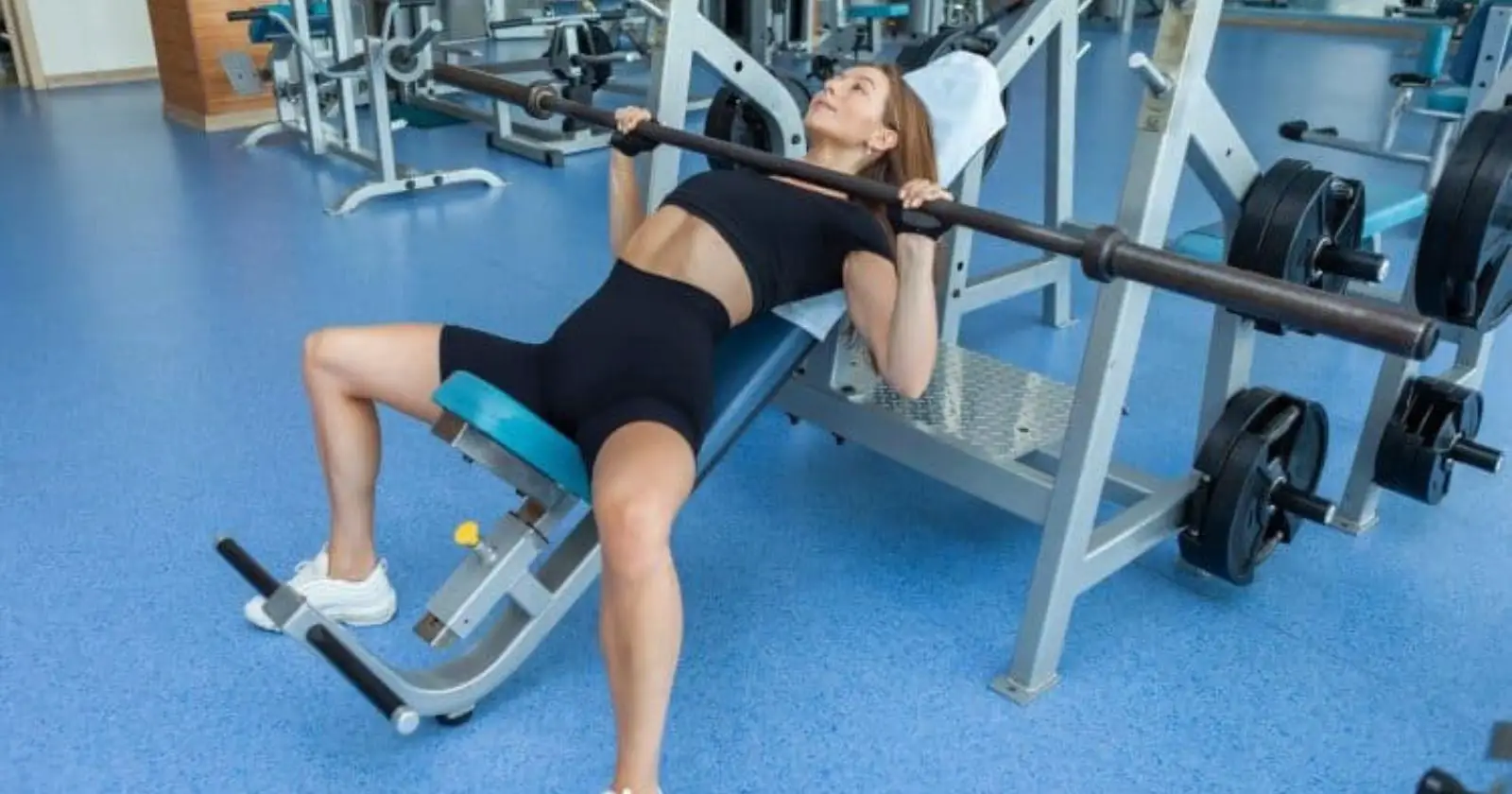
5. Overhead Press
The overhead press is a compound exercise that targets the shoulders and triceps. To perform an overhead press, stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and hold a barbell at shoulder height with an overhand grip. Push the barbell up overhead until your arms are fully extended, and then lower the barbell back down to the starting position.
Incorporating these top 5 compound exercises into your workout routine will help you build muscle and strength efficiently and effectively. Remember to start with lighter weights and focus on proper form to avoid injury and get the most out of each exercise.
Squat
Squat is a compound exercise that targets multiple muscle groups in the lower body, including the legs, glutes, hips, and quads. It also engages the lower back and core muscles for stability and balance. In this section, I will discuss the proper technique for performing a squat, the muscles worked during a squat, and some variations of the squat.
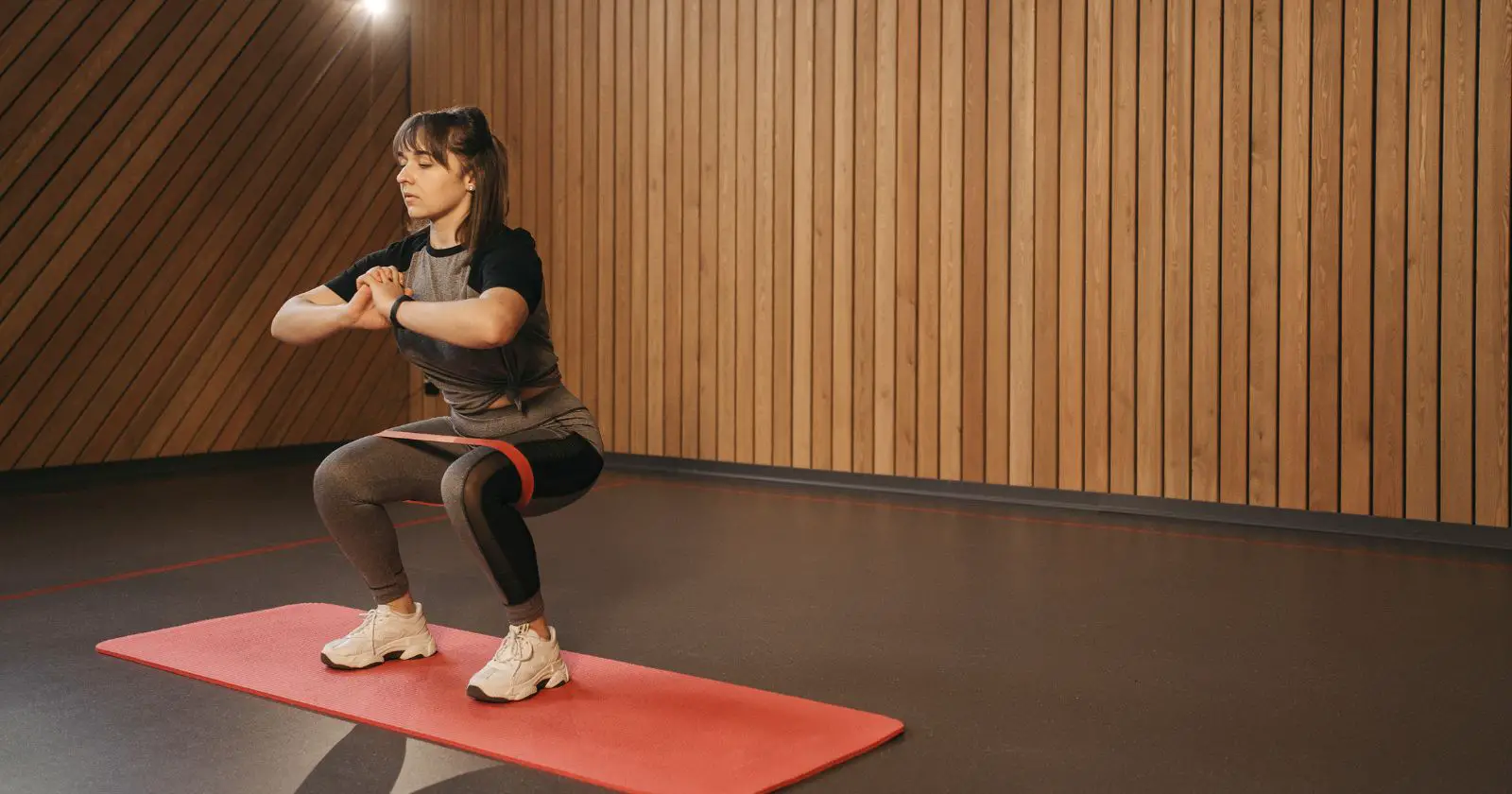

Squat Technique
When performing a squat, it is important to maintain proper technique to avoid injury and maximize the benefits of the exercise. Here are the steps to perform a squat correctly:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and your toes pointing slightly outward.
- Keep your chest up and your shoulders back, and engage your core muscles.
- Lower your body by bending your knees and pushing your hips back, as if you are sitting in a chair.
- Lower your body until your thighs are parallel to the ground or slightly below.
- Push through your heels and extend your legs to return to the starting position.
It is important to keep your knees in line with your toes and not let them cave inward. Also, avoid leaning forward or rounding your lower back.
Muscles Worked in Squat
Squat is a compound exercise that targets multiple muscle groups in the lower body. The primary muscles worked during a squat are:
- Quadriceps: The muscles on the front of your thighs that extend your knees.
- Glutes: The muscles in your buttocks that extend your hips.
- Hamstrings: The muscles on the back of your thighs that flex your knees.
- Calves: The muscles in your lower legs that help you push off the ground.
Squat also engages the lower back and core muscles for stability and balance.
Squat Variations
There are many variations of the squat that can target different muscle groups or add more challenge to the exercise. Here are some squat variations:
- Front Squat: This variation places more emphasis on the quadriceps and requires more core strength. Hold a barbell in front of your shoulders instead of on your back.
- Sumo Squat: This variation targets the inner thighs more. Stand with your feet wider than shoulder-width apart and your toes pointing outward.
- Bulgarian Split Squat: This variation targets each leg individually and requires more balance. Stand with one foot on a bench or step behind you and lower your body with the other leg.
- Pistol Squat: This variation targets each leg individually and requires more strength and balance. Stand on one leg and lower your body until your thigh is parallel to the ground.
In conclusion, squat is a compound exercise that targets multiple muscle groups in the lower body and engages the lower back and core muscles for stability and balance. By following proper technique and incorporating variations, you can maximize the benefits of this exercise.
Deadlift
The deadlift is a compound exercise that works several muscle groups, including the back, lats, hamstrings, glutes, hips, and lower back. It is considered one of the best exercises for building overall strength and power. In this section, I will cover the deadlift technique, muscles worked in the deadlift, and some popular deadlift variations.
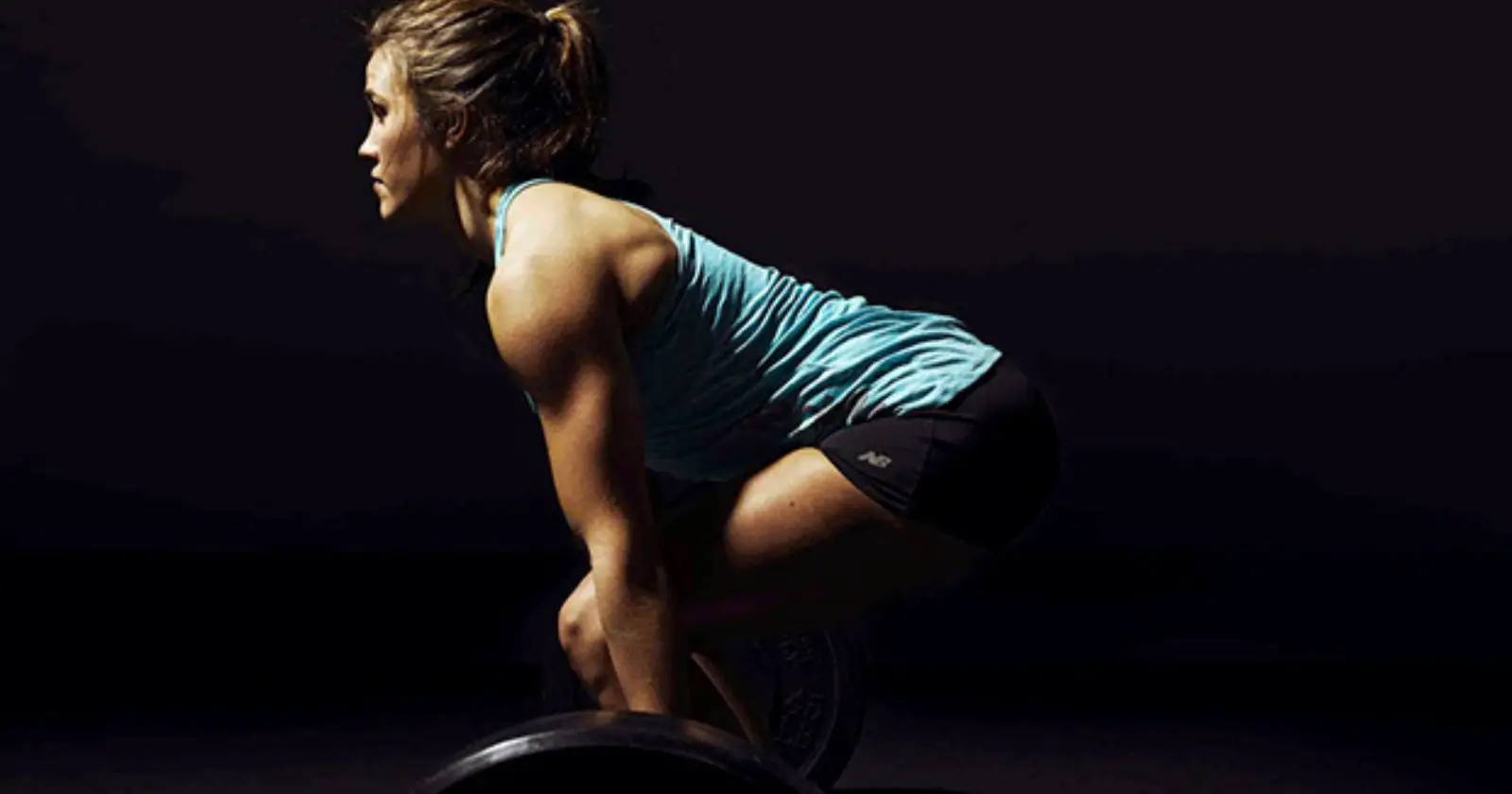

Deadlift Technique
To perform a deadlift, stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and your toes pointing forward. Place your hands on the barbell with an overhand or mixed grip, depending on your preference. Bend your knees and lower your hips until your shins touch the bar. Keep your back straight and your chest up.
Take a deep breath, brace your core, and lift the bar off the ground by driving your feet into the floor. Keep the bar close to your body as you stand up, extending your hips and knees. Squeeze your glutes at the top of the movement and then lower the bar back down to the ground in a controlled manner.
Muscles Worked in Deadlift
The deadlift is a full-body exercise that primarily works the posterior chain muscles, including the back, lats, hamstrings, glutes, and hips. It also engages the core, lower back, and grip muscles. The deadlift is a great exercise to improve overall strength and power.
Deadlift Variations
There are many different deadlift variations that you can use to target specific muscle groups or add variety to your training. Some popular deadlift variations include:
- Sumo Deadlift: This variation involves a wider stance and a more upright torso, which places more emphasis on the quads and inner thighs.
- Romanian Deadlift: This variation involves a slight bend in the knees and a greater emphasis on the hamstrings and glutes.
- Trap Bar Deadlift: This variation uses a trap bar, which allows for a more natural grip position and places less stress on the lower back.
- Deficit Deadlift: This variation involves standing on a raised platform, which increases the range of motion and places more emphasis on the hamstrings and glutes.
In conclusion, the deadlift is a powerful exercise that can help build overall strength and power. By using proper technique and incorporating different variations, you can target specific muscle groups and keep your training interesting and challenging.
Bench Press
The bench press is a classic upper body compound exercise that targets the chest, triceps, and shoulders. It is a popular exercise for building upper body strength and muscle mass. In this section, I will cover the bench press technique, the muscles worked in the bench press, and some of the bench press variations.
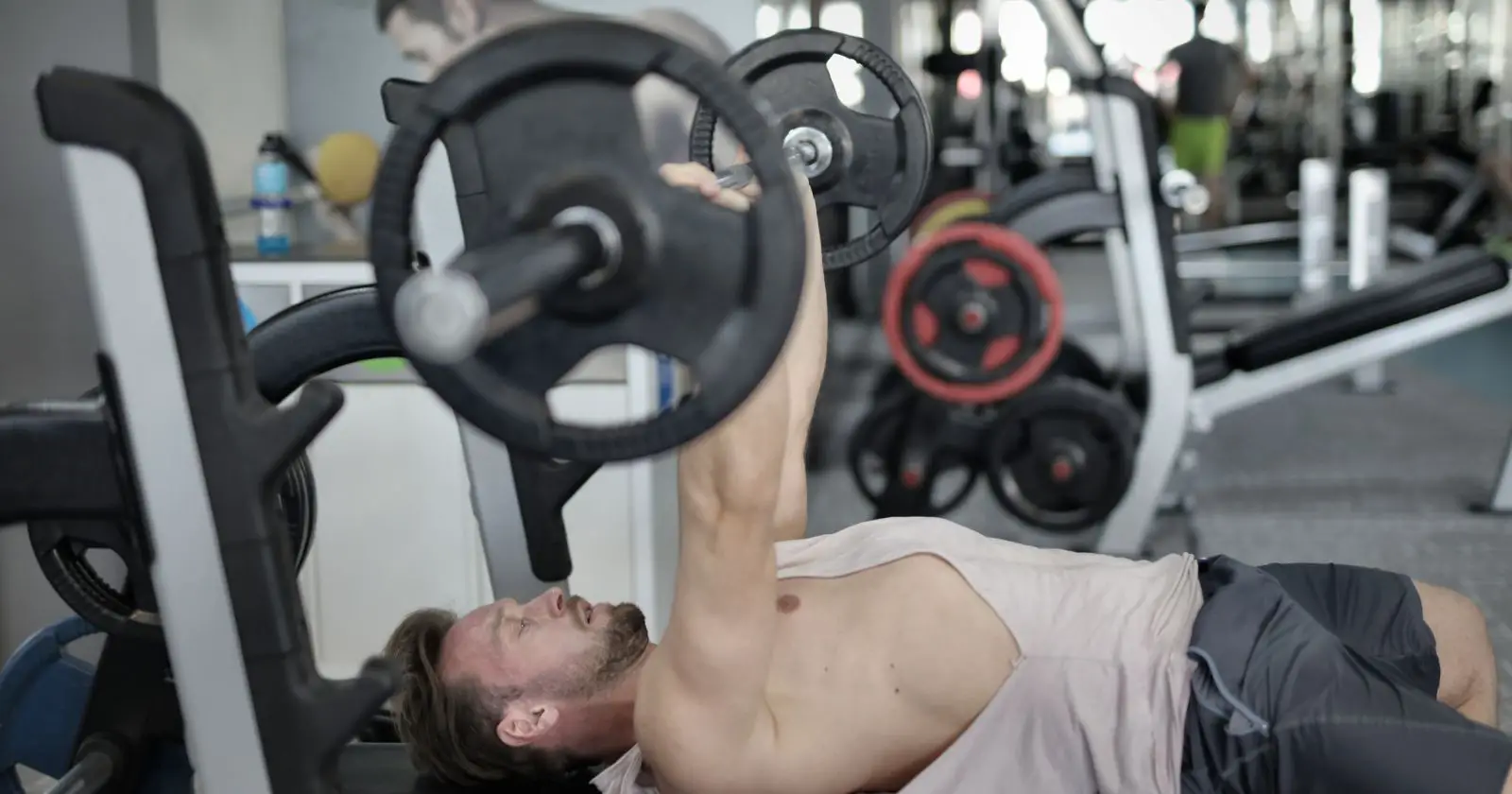

Bench Press Technique
To perform the bench press, lie on a flat bench with your feet flat on the ground. Grasp the barbell using an overhand grip, placing your thumbs on the outside of your closed fist. Your arms should be slightly wider than shoulder-width apart and the angle of your upper arms should be about 45 degrees to the body. Remove the barbell from the rack, locking your elbows. Do not move the bar in an arc from the rack directly to the chest position. Lower the barbell to your chest, keeping your elbows tucked in. Pause for a moment and then press the barbell back up to the starting position.
It is important to maintain proper form when performing the bench press. Keep your back flat on the bench, your feet planted firmly on the ground, and your core tight. Avoid arching your back or lifting your hips off the bench. Use a weight that allows you to perform the exercise with proper form and control.
Muscles Worked in Bench Press
The bench press primarily targets the chest muscles, specifically the pectoralis major and minor. However, it also works the triceps and shoulders as secondary muscles. The bench press is a compound exercise that engages multiple muscle groups in the upper body.
Bench Press Variations
There are several variations of the bench press that can be used to target different muscle groups or add variety to your workout routine. Some popular bench press variations include:
- Incline bench press: This variation targets the upper chest muscles more than the flat bench press.
- Decline bench press: This variation targets the lower chest muscles more than the flat bench press.
- Close-grip bench press: This variation places more emphasis on the triceps than the chest.
- Dumbbell bench press: This variation allows for a greater range of motion and can help to improve muscle imbalances.
Incorporating bench press variations into your workout routine can help to prevent boredom and challenge your muscles in new ways. It is important to choose the right variation for your fitness level and goals, and to use proper form when performing the exercise.
Pull-Up
Pull-Up Technique
The pull-up is a classic exercise that targets the back, biceps, and lats, making it an excellent upper body workout. To perform a pull-up, follow these steps:
- Begin by hanging from a pull-up bar with your palms facing away from you and your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
- Engage your back muscles and pull your body up towards the bar, keeping your elbows close to your body.
- Once your chin is above the bar, pause for a moment, then slowly lower yourself back down to the starting position.
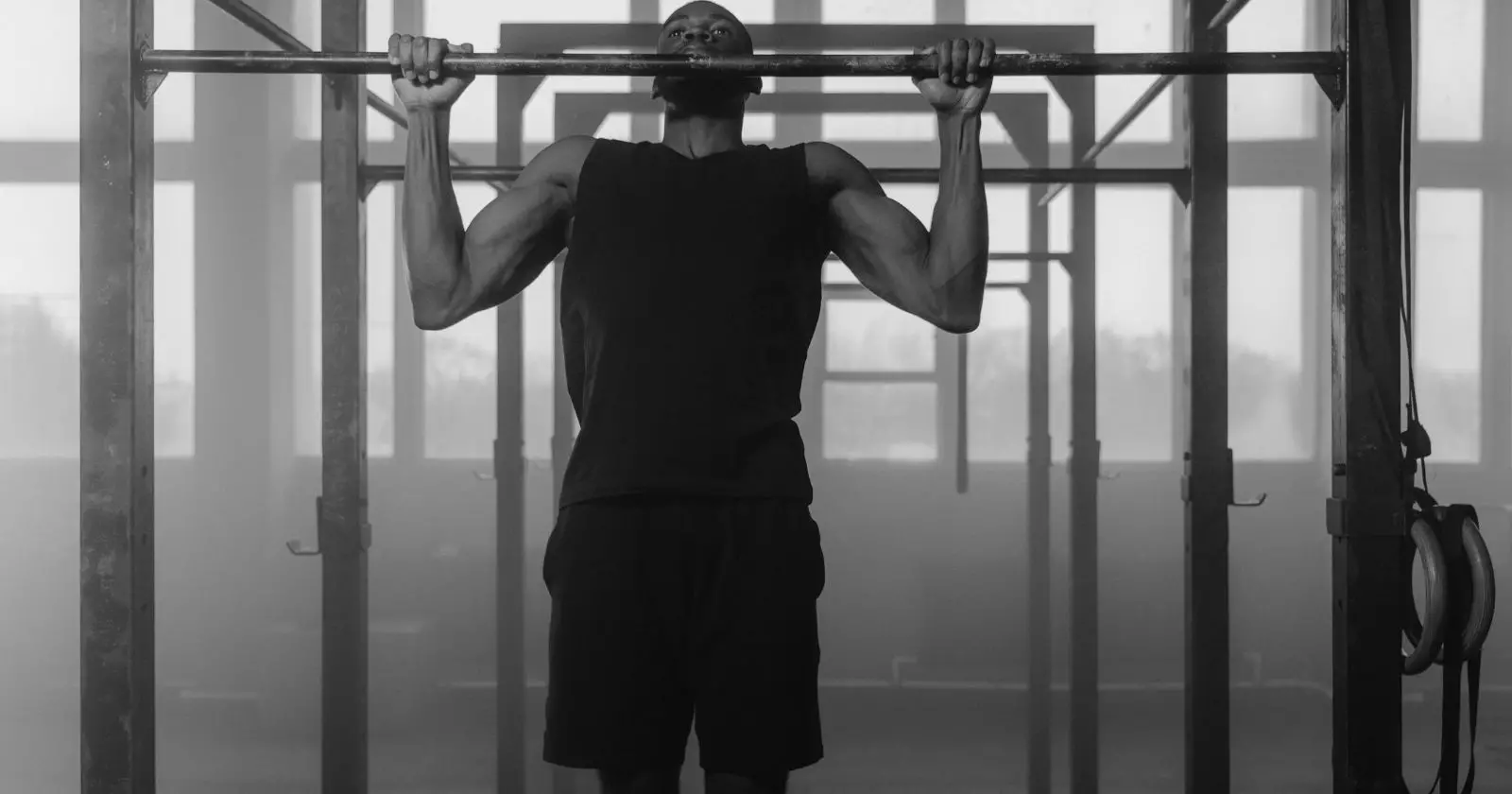

It’s important to maintain proper form throughout the exercise. Keep your core engaged, your shoulders down and back, and your chest lifted. Avoid swinging or using momentum to complete the movement.
Muscles Worked in Pull-Up
The pull-up primarily targets the back muscles, including the latissimus dorsi (lats), rhomboids, and traps. Additionally, the biceps and forearms are also engaged during the movement.
Pull-Up Variations
There are several variations of the pull-up that can be used to target different muscles or add variety to your workout. Here are a few examples:
- Wide-Grip Pull-Up: Perform a pull-up with your hands wider than shoulder-width apart to place more emphasis on the outer back muscles.
- Close-Grip Pull-Up: Perform a pull-up with your hands closer together to target the biceps and inner back muscles.
- Chin-Up: Perform a pull-up with your palms facing towards you to shift the focus to the biceps.
- Neutral-Grip Pull-Up: Perform a pull-up with your palms facing each other to reduce stress on the wrists and elbows.
Experiment with different variations to find what works best for you. Remember to always prioritize proper form and gradually increase the difficulty or intensity of the exercise as you become stronger.
Overhead Press
The overhead press is a compound exercise that targets the shoulders, triceps, and upper body. It is a classic exercise that has been used for decades to build upper body strength and muscle mass. In this section, I will cover the technique, muscles worked, and variations of the overhead press.
Overhead Press Technique
To perform the overhead press, start with your feet shoulder-width apart and the barbell resting on your shoulders. Your hands should be slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, and your elbows should be pointing forward. Next, push the barbell up and overhead until your arms are fully extended. Lower the barbell back down to your shoulders and repeat for the desired number of reps.
It is important to maintain proper form throughout the exercise. Keep your core engaged, and avoid arching your back. Also, make sure to keep your elbows pointing forward and not out to the sides.
Muscles Worked in Overhead Press
The overhead press primarily targets the shoulders, specifically the anterior and medial deltoids. It also works the triceps and upper chest to a lesser extent. Additionally, the overhead press engages the core muscles to stabilize the body during the movement.
Overhead Press Variations
There are several variations of the overhead press that can be used to target different muscle groups or add variety to your workout routine. Some popular variations include:
- Seated Overhead Press: This variation is performed while seated, which can help to isolate the shoulders and reduce strain on the lower back.
- Dumbbell Overhead Press: Using dumbbells instead of a barbell can help to increase range of motion and engage the stabilizer muscles.
- Push Press: The push press involves using a slight leg drive to help lift the weight overhead, which can allow for heavier weights to be used.
Overall, the overhead press is a great exercise for building upper body strength and muscle mass. By mastering the technique and incorporating variations into your routine, you can continue to challenge your muscles and see progress over time.
Benefits of Compound Exercises
As someone who has been working out for years, I can confidently say that compound exercises are one of the most effective ways to improve overall fitness. Compound exercises are movements that work multiple muscle groups at the same time, making them a great choice for anyone looking to build muscle mass, improve cardiovascular health, and increase overall strength.
One of the biggest benefits of compound exercises is that they burn more calories than isolation exercises. Because compound exercises work multiple muscle groups, they require more energy to perform, which means you’ll burn more calories during your workout. This makes compound exercises a great choice for anyone looking to lose weight or improve their overall fitness.
In addition to burning more calories, compound exercises also help improve balance and coordination. Because these exercises require you to use multiple muscle groups at the same time, they help improve your overall body awareness and control. This can help reduce the risk of injury during other activities and improve overall athletic performance.
Another benefit of compound exercises is that they promote muscle growth and development. Because these exercises work multiple muscle groups, they help stimulate the release of hormones like testosterone, which is essential for muscle growth and development. This makes compound exercises a great choice for anyone looking to build muscle mass and improve overall strength.
Overall, there are many benefits to incorporating compound exercises into your workout routine. Whether you’re looking to improve muscle mass, burn more calories, or improve overall fitness, compound exercises are a great choice. By working multiple muscle groups at the same time, these exercises offer a more efficient and effective way to improve overall health and wellness.
Incorporating Compound Exercises into Your Workout Routine
When it comes to building an effective workout routine, incorporating compound exercises is essential. These exercises work multiple muscle groups at once, making them more efficient and effective than isolation exercises. Here are a few tips for incorporating compound exercises into your workout routine:
Start with the Basics
If you’re new to compound exercises, start with the basics. Squats, deadlifts, and bench presses are all great compound exercises that work multiple muscle groups at once. They’re also relatively easy to learn and can be performed with free weights or in a gym setting.
Mix It Up
While the basics are a great place to start, it’s important to mix things up to keep your workouts interesting and challenging. Try incorporating different variations of the basic exercises, such as sumo squats or Romanian deadlifts. You can also try adding in other compound exercises, such as pull-ups or lunges.
Use Free Weights
While machines can be useful for certain exercises, free weights are generally better for compound exercises. Free weights require more stabilization and engage more muscle groups, making them more effective for building strength and muscle mass.

Focus on Form
Proper form is essential when performing compound exercises. Not only does it help prevent injury, but it also ensures that you’re targeting the right muscle groups. Take the time to learn proper form for each exercise and focus on maintaining it throughout your workouts.
Incorporate Mobility Work
Compound exercises can be tough on the body, so it’s important to incorporate mobility work into your routine. This can include stretching, foam rolling, or other mobility exercises that help keep your muscles and joints healthy and flexible.
Incorporating compound exercises into your workout routine can be a game-changer for building strength and muscle mass. By starting with the basics, mixing things up, using free weights, focusing on form, and incorporating mobility work, you can create a well-rounded routine that will help you reach your fitness goals.
Safety and Precautions
As with any exercise program, safety and precautions are paramount to prevent injury and ensure optimal results. Here are some important things to keep in mind when performing compound exercises:
Technique
Proper technique is essential when performing compound exercises to avoid injury and maximize results. It is important to maintain good form throughout each exercise, paying attention to your body’s alignment, balance, and coordination. If you are not sure about the correct technique, seek guidance from a qualified fitness professional or use online resources such as videos or tutorials.
Balance and Coordination
Compound exercises require balance and coordination to perform correctly. It is important to start with lighter weights and gradually increase the weight as you become more comfortable with the exercise. If you feel unsteady or lose your balance during an exercise, stop and regain your footing before continuing.

Mobility
Mobility is essential for performing compound exercises effectively. It is important to warm up properly before starting your workout to increase blood flow and prepare your muscles and joints for the exercises. Incorporating stretching exercises into your routine can also help improve your mobility and flexibility.
Joints and Spine
Compound exercises can put stress on your joints and spine, so it is important to use proper technique and avoid overloading the joints. It is also important to listen to your body and avoid pushing yourself too hard, especially if you have any pre-existing injuries or conditions.
In summary, compound exercises are a great way to improve your overall fitness and strength. By following these safety and precaution tips, you can perform these exercises safely and effectively to achieve your fitness goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some compound exercises for the back?
Compound exercises are great for targeting multiple muscle groups at once. Some compound exercises for the back include deadlifts, pull-ups, rows, and lat pulldowns. Deadlifts work the forearms, lats, glutes, hamstrings, core, upper-, mid-, and lower back. Pull-ups and rows target the upper back and lat pulldowns work the lats.
What is a good full-body compound workout routine?
A good full-body compound workout routine should include exercises that target multiple muscle groups at once. Some good compound exercises to include in a full-body workout routine are squats, lunges, deadlifts, bench press, shoulder press, bent-over rows, and pull-ups. It’s important to vary the exercises and the intensity of the workout to avoid plateauing.
Are there any compound exercises that can be done at home?
Yes, there are many compound exercises that can be done at home. Some examples include bodyweight squats, lunges, push-ups, pull-ups, bent-over rows, and burpees. You can also use resistance bands or dumbbells to add more resistance to your workouts.
What are some compound exercises for beginners?
Compound exercises are great for beginners because they work multiple muscle groups at once, which can help build overall strength and endurance. Some good compound exercises for beginners include squats, lunges, push-ups, pull-ups, bench press, and shoulder press. It’s important to start with light weights and focus on proper form to avoid injury.
For more exercises to explore, checkout this post on medicine ball workouts.

